1.Introduction :
We show here sample codes for performing Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) with OpenCL/GPU clMathLibraries. All sources for 1D, 2D and 3D cases are available into the following archive :
You will find also the FFTW version of OpenCL examples. Below the different cases :
2.Expression of Fourier transform :
General form of Fourier transform is :
\begin{equation}
\text{FT}\,[f(\vec{r})]=F(\vec{f})={\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\,f(\vec{r})\,e^{-j2\pi\,\vec{f}\cdot\vec{r}}\,\text{d}\vec{r}
\end{equation}
Caution, vector above $\vec{f}=(f_{x},f_{y},f_{z})$ represents the spatial frequencies, also defined with wavenumber by $\vec{k}=2\pi\vec{f}$ . In case of FT in temporal domain, components of $\vec{f}$ are temporal frequencies.
For each case below, we perform a FFT transform on a discrete cosinus or a product of discrete cosinus functions (depending dimension) . As an example into 2D case, function to discretize is :
\begin{equation}
f(x,y) = \cos(2\pi f_{1}x)\,\cos(2\pi f_{2}y)
\end{equation}
$\qquad\qquad\qquad$FT is expressed as follows :
\begin{eqnarray}
\begin{aligned}
\text{TF}\,[f(x,y)]&=F(f_{x},f_{y})={\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\,f(x,y)\,e^{-j 2\pi\,\vec{f}\cdot\vec{r}}\,\text{d}\vec{r}\\
&={\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}{\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\,f(x,y)\,e^{-j 2\pi f_{x}x}\,e^{-j 2\pi f_{y}y}\,\text{d}x\,\text{d}y\\
&={\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\cos(2\pi f_{1}x)\,e^{-j 2\pi f_{x}x}\,\text{d}x\,{\large\int}_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\cos(2\pi f_{2}y)\,e^{-j 2\pi f_{y}y}\,\text{d}y\\
&=\dfrac{1}{4}\big[\delta(f_{x}-f_{1})+\delta(f_{x}+f_{1})\big]\,\big[\delta(f_{y}-f_{2})+\delta(f_{y}+f_{2})\big]
\end{aligned}
\end{eqnarray}
Finally, we get a product of Dirac's functions, each of one with a different frequency ($f{_1}$ and $f_{2}$). We will validate this result in discrete case.
We take a simple cosinus input signal with a 10 Hz frequency and a sampling frequency of 1000 Hz, so a signal sampled on 100 points. If you want to modify these parameters, make sure to verify the Shannon theorem by respecting Fsampling > 2 Fmax,signal. We apply firstly a forward FFT and then a backward transformation to see if we get back the initial input signal.
1 #include "clFFT.h"
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <math.h>
6
7
8
9
10
11 int FFT_1D_OpenCL(float *tab[], const char* direction, int size) {
12
13
14 int i;
15
16
17 cl_int err;
18 cl_platform_id platform = 0;
19 cl_device_id device = 0;
20 cl_context ctx = 0;
21 cl_command_queue queue = 0;
22
23
24 cl_mem buffersIn[2] = {0, 0};
25 cl_mem buffersOut[2] = {0, 0};
26
27
28 cl_mem tmpBuffer = 0;
29
30
31 size_t tmpBufferSize = 0;
32 int status = 0;
33 int ret = 0;
34
35
36 size_t N = size;
37
38
39 clfftPlanHandle planHandle;
40 clfftDim dim = CLFFT_1D;
41 size_t clLengths[1] = {N};
42
43
44 err = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform, NULL);
45 err = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 1, &device, NULL);
46
47
48 ctx = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, &err);
49
50
51 queue = clCreateCommandQueueWithProperties(ctx, device, 0, &err);
52
53
54 clfftSetupData fftSetup;
55 err = clfftInitSetupData(&fftSetup);
56 err = clfftSetup(&fftSetup);
57
58
59 err = clfftCreateDefaultPlan(&planHandle, ctx, dim, clLengths);
60
61
62 err = clfftSetPlanPrecision(planHandle, CLFFT_SINGLE);
63 err = clfftSetLayout(planHandle, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR);
64 err = clfftSetResultLocation(planHandle, CLFFT_OUTOFPLACE);
65
66
67 err = clfftBakePlan(planHandle, 1, &queue, NULL, NULL);
68
69
70 cl_float* inReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
71 cl_float* inImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
72 cl_float* outReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
73 cl_float* outImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
74
75
76 for(i=0; i<N; i++)
77 {
78 inReal[i] = tab[0][i];
79 inImag[i] = 0.0f;
80 outReal[i] = 0.0f;
81 outImag[i] = 0.0f;
82 }
83
84
85 status = clfftGetTmpBufSize(planHandle, &tmpBufferSize);
86
87 if ((status == 0) && (tmpBufferSize > 0)) {
88 tmpBuffer = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, tmpBufferSize, 0, &err);
89 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
90 printf("Error with tmpBuffer clCreateBuffer\n");
91 }
92
93
94 buffersIn[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
95 N * sizeof(cl_float), inReal, &err);
96 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
97 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
98
99
100 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N *
101 sizeof(float),
102 inReal, 0, NULL, NULL);
103 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
104 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
105
106
107 buffersIn[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
108 N * sizeof(cl_float), inImag, &err);
109 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
110 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
111
112
113 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float),
114 inImag, 0, NULL, NULL);
115 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
116 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
117
118
119 buffersOut[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
120 sizeof(cl_float), outReal, &err);
121 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
122 printf("Error with buffersOut[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
123
124 buffersOut[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
125 sizeof(cl_float), outImag, &err);
126 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
127 printf("Error with buffersOut[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
128
129
130 if(strcmp(direction,"forward") == 0)
131 {
132
133 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_FORWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
134 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
135 }
136 else if(strcmp(direction,"backward") == 0)
137 {
138
139 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_BACKWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
140 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
141 }
142
143
144 err = clFinish(queue);
145
146
147 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[0],
148 0, NULL, NULL);
149 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[1],
150 0, NULL, NULL);
151
152
153 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[0]);
154 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[1]);
155 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[0]);
156 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[1]);
157 clReleaseMemObject(tmpBuffer);
158
159
160 err = clfftDestroyPlan(&planHandle);
161
162
163 clfftTeardown();
164
165
166 clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
167 clReleaseContext(ctx);
168
169 return ret;
170 }
171
172 int main(void) {
173
174
175 int i;
176
177
178 float *Array[2];
179
180
181 int size = 100;
182
183
184 float h = 0;
185
186
187 float frequency_signal = 10;
188
189
190 float frequency_sampling = size*frequency_signal;
191
192
193 float step = 1.0/frequency_sampling;
194
195
196 FILE *FFT_1D;
197
198
199 Array[0] = (float*) malloc(size*sizeof(float));
200 Array[1] = (float*) malloc(size*sizeof(float));
201
202
203 FFT_1D = fopen("FFT_1D_OpenCL_Input.dat","w");
204 for(i=0; i<size; i++)
205 {
206 Array[0][i] = cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signal*h);
207 Array[1][i] = 0.0f;
208 fprintf(FFT_1D,"%f %e\n",i/(frequency_signal*size),Array[0][i]);
209 h = h + step;
210 }
211 fclose(FFT_1D);
212
213
214 if (FFT_1D_OpenCL(Array,"forward", size) == 0)
215 printf("FFT passed !\n");
216
217
218 FFT_1D = fopen("FFT_1D_OpenCL_Forward.dat","w");
219 for (i=0; i<size; i++)
220 fprintf(FFT_1D,"%f %e\n", i*frequency_sampling/size, Array[0][i]);
221 fclose(FFT_1D);
222
223
224 if (FFT_1D_OpenCL(Array,"backward", size) == 0)
225 printf("IFFT passed !\n");
226
227
228 FFT_1D = fopen("FFT_1D_OpenCL_Backward.dat","w");
229 for (i=0; i<size; i++)
230 fprintf(FFT_1D,"%f %e\n", i/(size*frequency_signal), Array[0][i]);
231 fclose(FFT_1D);
232
233 return 0;
234 }
|
On the figure below the plot with plot_fft1d.m of the three operations : the input signal, its spectrum and the final output after the inverse transformation of the first FFT :
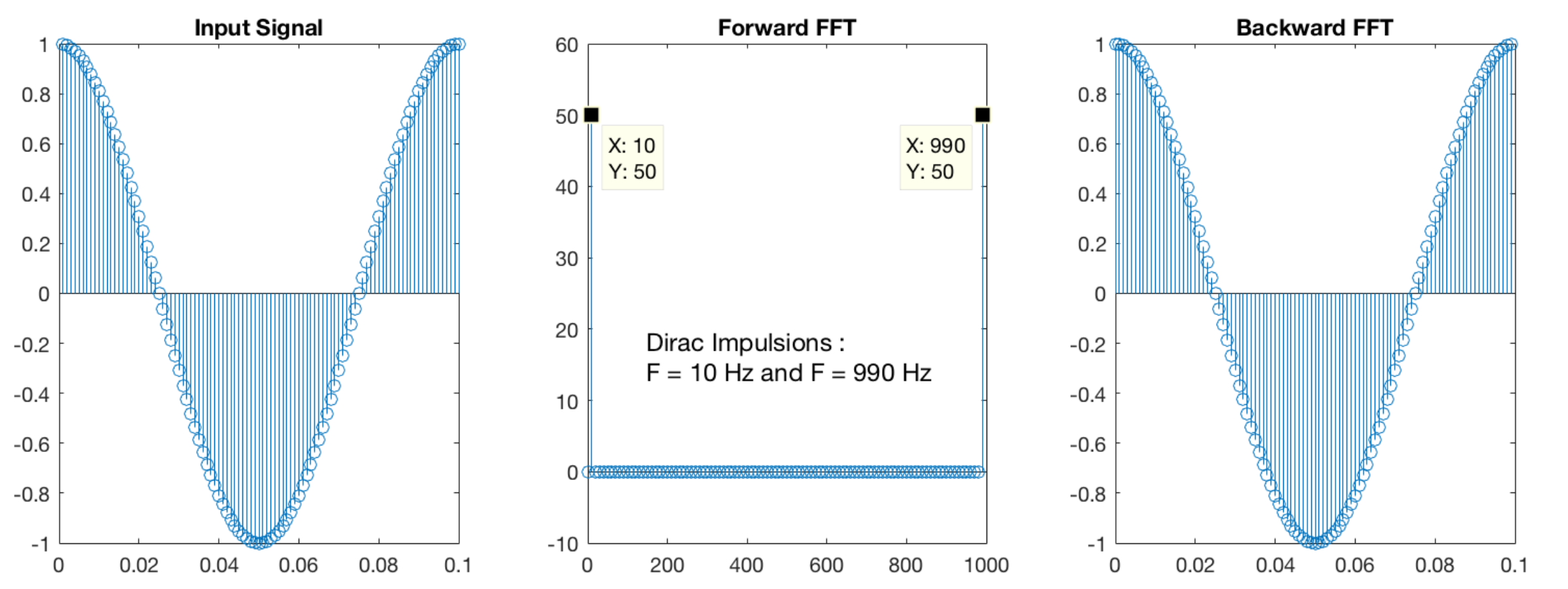
Concerning the spectrum, we have well Dirac impulsions at F = 10Hz and F = Fsampling - 10 = 990Hz. Figure on the right validates also the good working of backward FFT because the output signal is the same as input.
Following the 1D example, we take again a 2D cosinus signal (product of two cosinus) with a 10 Hz frequency on x axis and 20 Hz on y axis, and respectively a sampling frequency of 1000 Hz and 4000 Hz. Here is the sample code :
1 #include "clFFT.h"
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <math.h>
6
7
8
9
10
11 int FFT_2D_OpenCL(float *tab[], const char* direction, int sizex, int sizey) {
12
13
14 int i;
15
16
17 cl_int err;
18 cl_platform_id platform = 0;
19 cl_device_id device = 0;
20 cl_context ctx = 0;
21 cl_command_queue queue = 0;
22
23
24 cl_mem buffersIn[2] = {0, 0};
25 cl_mem buffersOut[2] = {0, 0};
26
27
28 cl_mem tmpBuffer = 0;
29
30
31 size_t tmpBufferSize = 0;
32 int status = 0;
33 int ret = 0;
34
35
36 size_t N = sizex*sizey;
37
38
39 clfftPlanHandle planHandle;
40 clfftDim dim = CLFFT_2D;
41 size_t clLengths[2] = {sizex, sizey};
42
43
44 err = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform, NULL);
45 err = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 1, &device, NULL);
46
47
48 ctx = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, &err);
49
50
51 queue = clCreateCommandQueueWithProperties(ctx, device, 0, &err);
52
53
54 clfftSetupData fftSetup;
55 err = clfftInitSetupData(&fftSetup);
56 err = clfftSetup(&fftSetup);
57
58
59 err = clfftCreateDefaultPlan(&planHandle, ctx, dim, clLengths);
60
61
62 err = clfftSetPlanPrecision(planHandle, CLFFT_SINGLE);
63 err = clfftSetLayout(planHandle, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR);
64 err = clfftSetResultLocation(planHandle, CLFFT_OUTOFPLACE);
65
66
67 err = clfftBakePlan(planHandle, 1, &queue, NULL, NULL);
68
69
70 cl_float* inReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
71 cl_float* inImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
72 cl_float* outReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
73 cl_float* outImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
74
75
76 for(i=0; i<N; i++)
77 {
78 inReal[i] = tab[0][i];
79 inImag[i] = 0.0f;
80 outReal[i] = 0.0f;
81 outImag[i] = 0.0f;
82 }
83
84
85 status = clfftGetTmpBufSize(planHandle, &tmpBufferSize);
86
87 if ((status == 0) && (tmpBufferSize > 0)) {
88 tmpBuffer = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, tmpBufferSize, 0, &err);
89 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
90 printf("Error with tmpBuffer clCreateBuffer\n");
91 }
92
93
94 buffersIn[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
95 N * sizeof(cl_float), inReal, &err);
96 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
97 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
98
99
100 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N *
101 sizeof(float),
102 inReal, 0, NULL, NULL);
103 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
104 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
105
106
107 buffersIn[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
108 N * sizeof(cl_float), inImag, &err);
109 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
110 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
111
112
113 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float),
114 inImag, 0, NULL, NULL);
115 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
116 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
117
118
119 buffersOut[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
120 sizeof(cl_float), outReal, &err);
121 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
122 printf("Error with buffersOut[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
123
124 buffersOut[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
125 sizeof(cl_float), outImag, &err);
126 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
127 printf("Error with buffersOut[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
128
129
130 if(strcmp(direction,"forward") == 0)
131 {
132
133 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_FORWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
134 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
135 }
136 else if(strcmp(direction,"backward") == 0)
137 {
138
139 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_BACKWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
140 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
141 }
142
143
144 err = clFinish(queue);
145
146
147 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[0],
148 0, NULL, NULL);
149 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[1],
150 0, NULL, NULL);
151
152
153 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[0]);
154 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[1]);
155 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[0]);
156 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[1]);
157 clReleaseMemObject(tmpBuffer);
158
159
160 err = clfftDestroyPlan(&planHandle);
161
162
163 clfftTeardown();
164
165
166 clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
167 clReleaseContext(ctx);
168
169 return ret;
170 }
171
172 int main(void) {
173
174
175 int i,j;
176
177
178 float *Array[2];
179
180
181 int sizex = 100;
182 int sizey = 200;
183
184
185 int N = sizex*sizey;
186
187
188 float hx = 0;
189 float hy = 0;
190
191
192 float frequency_signalx = 10;
193 float frequency_signaly = 20;
194
195
196 float frequency_samplingx = sizex*frequency_signalx;
197 float frequency_samplingy = sizey*frequency_signaly;
198
199
200 float stepx = 1.0/frequency_samplingx;
201 float stepy = 1.0/frequency_samplingy;
202
203
204 FILE *FFT_2D;
205
206
207 Array[0] = (float*) malloc(N*sizeof(float));
208 Array[1] = (float*) malloc(N*sizeof(float));
209
210
211 FFT_2D = fopen("FFT_2D_OpenCL_Input.dat","w");
212 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
213 {
214 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
215 {
216 Array[0][j*sizex+i] = cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signalx*hx)*
217 cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signaly*hy);
218 Array[1][j*sizex+i] = 0.0f;
219 fprintf(FFT_2D,"%f %f %e\n", i/(frequency_signalx*sizex),
220 j/(frequency_signaly*sizey),
221 Array[0][j*sizex+i]);
222 hx = hx + stepx;
223 }
224 hx = 0.0f;
225 hy = hy + stepy;
226 }
227 fclose(FFT_2D);
228
229
230 if (FFT_2D_OpenCL(Array,"forward", sizex, sizey) == 0)
231 printf("FFT passed !\n");
232
233
234 FFT_2D = fopen("FFT_2D_OpenCL_Forward.dat","w");
235 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
236 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
237 fprintf(FFT_2D,"%f %f %e\n", i*frequency_samplingx/sizex,
238 j*frequency_samplingy/sizey,
239 Array[0][j*sizex+i]);
240 fclose(FFT_2D);
241
242
243 if (FFT_2D_OpenCL(Array,"backward", sizex, sizey) == 0)
244 printf("IFFT passed !\n");
245
246
247 FFT_2D = fopen("FFT_2D_OpenCL_Backward.dat","w");
248 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
249 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
250 fprintf(FFT_2D,"%f %f %e\n", i/(frequency_signalx*sizex),
251 j/(frequency_signaly*sizey),
252 Array[0][j*sizex+i]);
253 fclose(FFT_2D);
254
255 return 0;
256 }
|
On the figure below the plot with plot_fft2d.m of the three operations : the input signal, its spectrum and the final output after the inverse transformation of the first FFT :
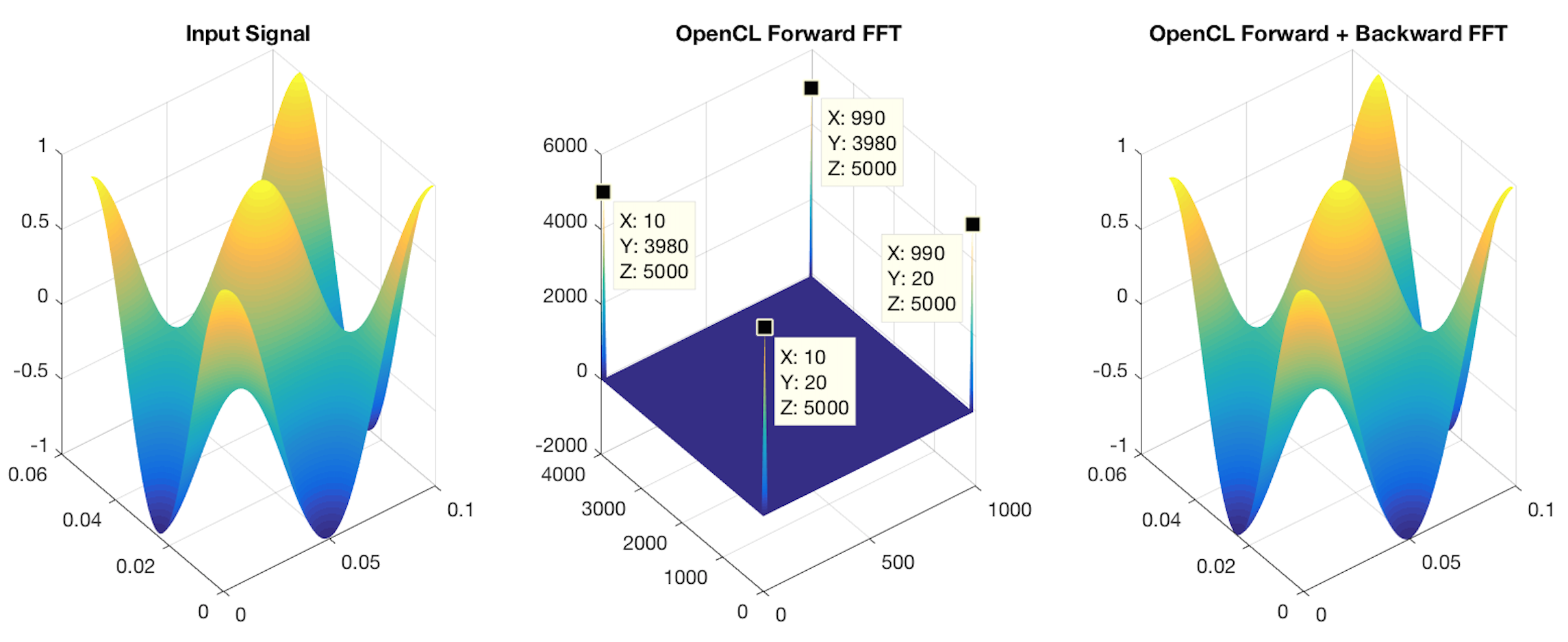
On the spectrum, we get Dirac impulsions of the product of two Dirac, one located at F = 10Hz and the other at F = 20 Hz. We can see also the other impulsions associated to Fsampling - Fx,signal and Fsampling - Fy,signal. Figure on the right validates also the good working of backward FFT because the output signal is the same as input.
For this case, we take a 3D cosinus signal (product of 3 cosinus) of frequencies 1Hz, 2Hz and 4Hz with sampling frequencies of 10Hz, 40Hz and 160Hz respectively along Ox, Oy and Oz direction. Here is the sample code :
1 #include "clFFT.h"
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <math.h>
6
7
8
9
10
11 int FFT_3D_OpenCL(float *tab[], const char* direction, int sizex, int sizey, int sizez) {
12
13
14 int i;
15
16
17 cl_int err;
18 cl_platform_id platform = 0;
19 cl_device_id device = 0;
20 cl_context ctx = 0;
21 cl_command_queue queue = 0;
22
23
24 cl_mem buffersIn[2] = {0, 0};
25 cl_mem buffersOut[2] = {0, 0};
26
27
28 cl_mem tmpBuffer = 0;
29
30
31 size_t tmpBufferSize = 0;
32 int status = 0;
33 int ret = 0;
34
35
36 size_t N = sizex*sizey*sizez;
37
38
39 clfftPlanHandle planHandle;
40 clfftDim dim = CLFFT_3D;
41 size_t clLengths[3] = {sizex, sizey, sizez};
42
43
44 err = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform, NULL);
45 err = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 1, &device, NULL);
46
47
48 ctx = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, &err);
49
50
51 queue = clCreateCommandQueueWithProperties(ctx, device, 0, &err);
52
53
54 clfftSetupData fftSetup;
55 err = clfftInitSetupData(&fftSetup);
56 err = clfftSetup(&fftSetup);
57
58
59 err = clfftCreateDefaultPlan(&planHandle, ctx, dim, clLengths);
60
61
62 err = clfftSetPlanPrecision(planHandle, CLFFT_SINGLE);
63 err = clfftSetLayout(planHandle, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR, CLFFT_COMPLEX_PLANAR);
64 err = clfftSetResultLocation(planHandle, CLFFT_OUTOFPLACE);
65
66
67 err = clfftBakePlan(planHandle, 1, &queue, NULL, NULL);
68
69
70 cl_float* inReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
71 cl_float* inImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
72 cl_float* outReal = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
73 cl_float* outImag = (cl_float*) malloc (N * sizeof (cl_float));
74
75
76 for(i=0; i<N; i++)
77 {
78 inReal[i] = tab[0][i];
79 inImag[i] = 0.0f;
80 outReal[i] = 0.0f;
81 outImag[i] = 0.0f;
82 }
83
84
85 status = clfftGetTmpBufSize(planHandle, &tmpBufferSize);
86
87 if ((status == 0) && (tmpBufferSize > 0)) {
88 tmpBuffer = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, tmpBufferSize, 0, &err);
89 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
90 printf("Error with tmpBuffer clCreateBuffer\n");
91 }
92
93
94 buffersIn[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
95 N * sizeof(cl_float), inReal, &err);
96 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
97 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
98
99
100 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N *
101 sizeof(float),
102 inReal, 0, NULL, NULL);
103 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
104 printf("Error with buffersIn[0] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
105
106
107 buffersIn[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
108 N * sizeof(cl_float), inImag, &err);
109 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
110 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
111
112
113 err = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, buffersIn[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float),
114 inImag, 0, NULL, NULL);
115 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
116 printf("Error with buffersIn[1] clEnqueueWriteBuffer\n");
117
118
119 buffersOut[0] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
120 sizeof(cl_float), outReal, &err);
121 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
122 printf("Error with buffersOut[0] clCreateBuffer\n");
123
124 buffersOut[1] = clCreateBuffer(ctx, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, N *
125 sizeof(cl_float), outImag, &err);
126 if (err != CL_SUCCESS)
127 printf("Error with buffersOut[1] clCreateBuffer\n");
128
129
130 if(strcmp(direction,"forward") == 0)
131 {
132
133 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_FORWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
134 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
135 }
136 else if(strcmp(direction,"backward") == 0)
137 {
138
139 err = clfftEnqueueTransform(planHandle, CLFFT_BACKWARD, 1, &queue, 0, NULL, NULL,
140 buffersIn, buffersOut, tmpBuffer);
141 }
142
143
144 err = clFinish(queue);
145
146
147 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[0], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[0],
148 0, NULL, NULL);
149 err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, buffersOut[1], CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), tab[1],
150 0, NULL, NULL);
151
152
153 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[0]);
154 clReleaseMemObject(buffersIn[1]);
155 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[0]);
156 clReleaseMemObject(buffersOut[1]);
157 clReleaseMemObject(tmpBuffer);
158
159
160 err = clfftDestroyPlan(&planHandle);
161
162
163 clfftTeardown();
164
165
166 clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
167 clReleaseContext(ctx);
168
169 return ret;
170 }
171
172 int main(void) {
173
174
175 int i,j,k;
176
177
178 float *Array[2];
179
180
181 int sizex = 10;
182 int sizey = 20;
183 int sizez = 40;
184
185
186 int N = sizex*sizey*sizez;
187
188
189 float hx = 0;
190 float hy = 0;
191 float hz = 0;
192
193
194 float frequency_signalx = 1;
195 float frequency_signaly = 2;
196 float frequency_signalz = 4;
197
198
199 float frequency_samplingx = sizex*frequency_signalx;
200 float frequency_samplingy = sizey*frequency_signaly;
201 float frequency_samplingz = sizez*frequency_signalz;
202
203
204 float stepx = 1.0/frequency_samplingx;
205 float stepy = 1.0/frequency_samplingy;
206 float stepz = 1.0/frequency_samplingz;
207
208
209 FILE *FFT_3D;
210
211
212 Array[0] = (float*) malloc(N*sizeof(float));
213 Array[1] = (float*) malloc(N*sizeof(float));
214
215
216 FFT_3D = fopen("FFT_3D_OpenCL_Input.dat","w");
217 for(k=0; k<sizez; k++)
218 {
219 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
220 {
221 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
222 {
223 Array[0][k*sizex*sizey+j*sizex+i] = cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signalx*hx)*
224 cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signaly*hy)*
225 cos(2*M_PI*frequency_signalz*hz);
226 Array[1][k*sizex*sizey+j*sizex+i] = 0.0f;
227 fprintf(FFT_3D,"%f %f %f %e\n", i/(frequency_signalx*sizex),
228 j/(frequency_signaly*sizey),
229 k/(frequency_signalz*sizez),
230 Array[0][k*sizex*sizey+j*sizex+i]);
231 hx = hx + stepx;
232 }
233 hx = 0.0f;
234 hy = hy + stepy;
235 }
236 hy=0.0f;
237 hz = hz + stepz;
238 }
239 fclose(FFT_3D);
240
241
242 if (FFT_3D_OpenCL(Array,"forward", sizex, sizey, sizez) == 0)
243 printf("FFT passed !\n");
244
245
246 FFT_3D = fopen("FFT_3D_OpenCL_Forward.dat","w");
247 for(k=0; k<sizez; k++)
248 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
249 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
250 fprintf(FFT_3D,"%f %f %f %e\n", i*frequency_samplingx/sizex,
251 j*frequency_samplingy/sizey,
252 k*frequency_samplingz/sizez,
253 Array[0][k*sizex*sizey+j*sizex+i]);
254 fclose(FFT_3D);
255
256
257 if (FFT_3D_OpenCL(Array,"backward", sizex, sizey, sizez) == 0)
258 printf("IFFT passed !\n");
259
260
261 FFT_3D = fopen("FFT_3D_OpenCL_Backward.dat","w");
262 for(k=0; k<sizez; k++)
263 for(j=0; j<sizey; j++)
264 for(i=0; i<sizex; i++)
265 fprintf(FFT_3D,"%f %f %f %e\n", i/(frequency_signalx*sizex),
266 j/(frequency_signaly*sizey),
267 k/(frequency_signalz*sizez),
268 Array[0][k*sizex*sizey+j*sizex+i]);
269 fclose(FFT_3D);
270
271 return 0;
272 }
|
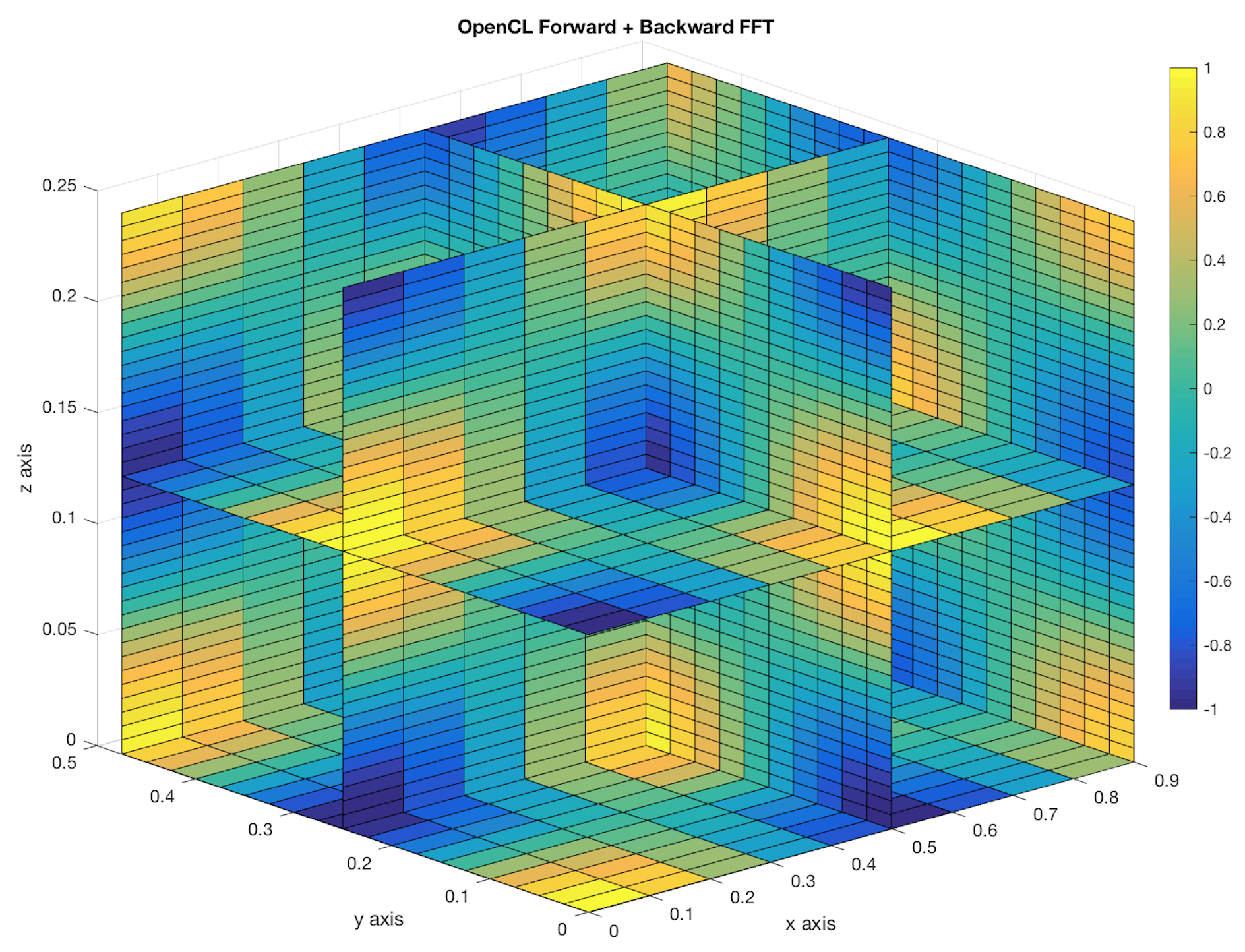
You can see below the slice plot of input signal and scatter plot of its spectrum (see plot_fft3d.m)
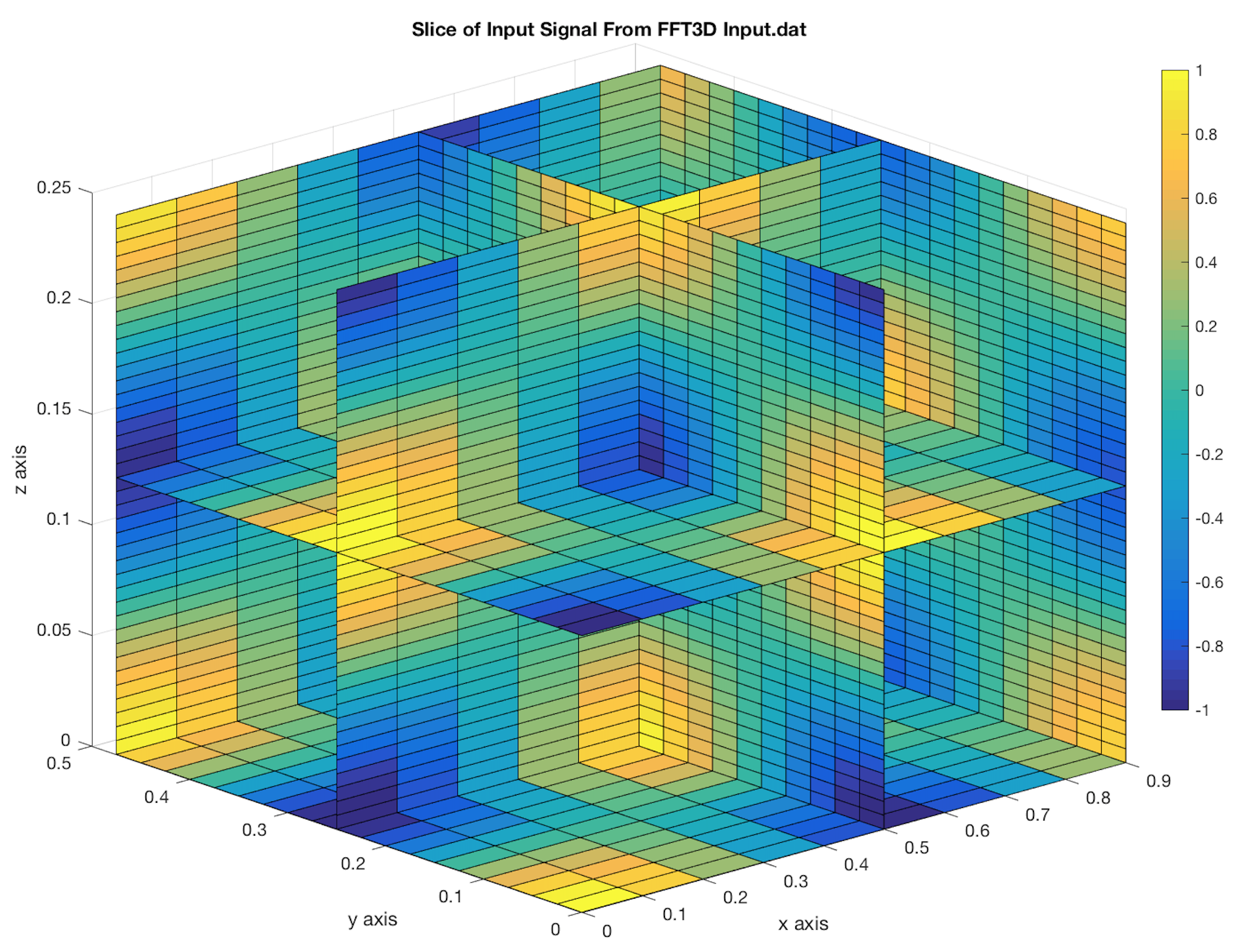
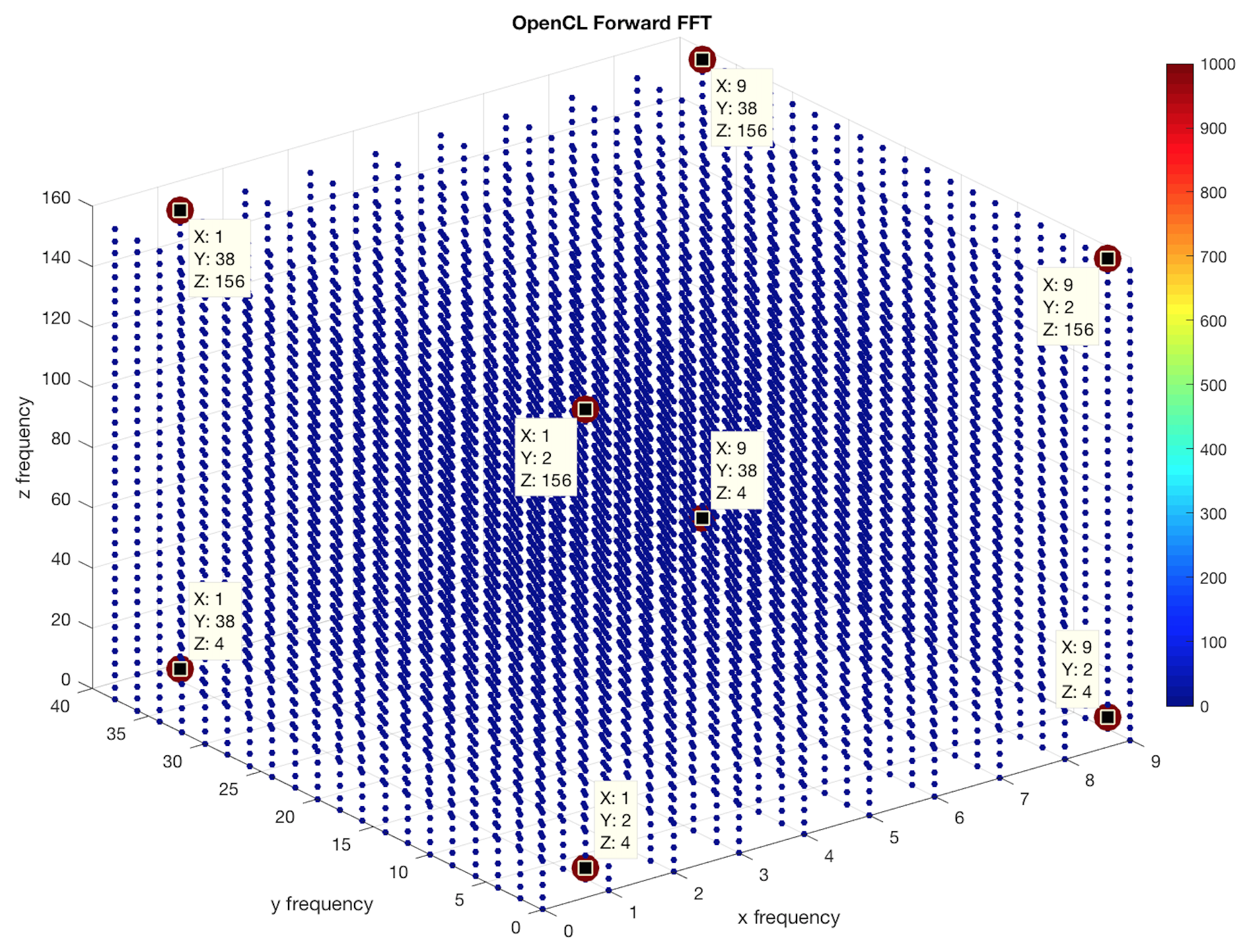
The second figure shows Dirac impulsions corresponding to the 3 Dirac product : one located at 1Hz, another at 2Hz and the last one at 4Hz. We get also the other associated impulsions at Fx,sampling - Fx,signal, Fy,sampling - Fy,signal and Fz,sampling - Fz,signal.
Finally, we validate the good achievement of Inverse FFT by checking below the backward transformation of first FFT : we get back the original input cosinus signal.
|








